

Risk and Crisis Management
Importance And Mission
PTTEP attaches great importance to Risk Management which is part of the Company’s main components of Governance, Risk Management, and Compliance (GRC) under the Sustainability Framework to ensure the achievement of our vision, mission, strategy, and business objectives as well as to respond appropriately to stakeholders’ expectations. The main aim is to promote sustainable growth and create short-term and long-term value for stakeholders. Therefore, risk management framework and policy have been established to ensure that the Company adopts good risk governance and risk management policy that all members of the management and employees must adhere to.
GOALS
High-impact Risk Identification with Effective Mitigation. This goal was approved by the Board Level.
Management Approach
Risk Governance
Having effective and efficient risk management as its commitment, the Board of Directors approved the Risk Governance Framework to define oversight responsibilities and authorities that demonstrate strong coordination, collaboration and communication among the board level, the management and business unit level for managing all aspects of risk in accordance with PTTEP’s policies effectively. In addition, the Board of Directors also approves the Risk Appetite Statement to be used as a framework for all PTTEP business operations and seeking business opportunities with acceptable risks. Ultimately, PTTEP intends to ensure that strategic risks, risks with high impact to corporate level (Corporate Risk), and emerging risks are well managed to prevent the arising of negative surprises, to reduce potential losses, and to minimize recurrence risks.
In 2024, PTTEP reviewed the Risk Management Committee Charter, the Risk Governance Framework, the Risk Appetite Statement, Corporate Level Risk Metrics and Limits, and the Enterprise Risk Management Policy, ensuring they reflected the implementation of the strategic plan and aligned with the evolving business objectives. The improvements were based on 3 sources including (1) the current practices and recommendations from the Risk Management Committee (RMC) and the Management Committee (MC); (2) the Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) Maturity Assessment; and (3) the Institute of Risk Management (IRM) in accordance with relevant international risk management standards.
PTTEP establishes its Enterprise Risk Management Policy and Framework approved by the Board Level Risk Management Committee that emphasize proactive risk management practices and a strong risk culture and establishes systematic Risk Management Process that is aligned with international standard ISO 31000:2018. In addition, the frameworks of the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO) Enterprise Risk Management – Integrating with Strategy and Performance (COSO ERM 2017) and COSO Enterprise Risk Management – Applying Enterprise Risk Management to Environmental, Social and Governance-related Risks (COSO ESG 2018) have been applied to enhance integration of enterprise risk management, strategic planning, and ESG-related risk management. PTTEP management and employees at all levels have responsibility with regard to effective risk management and promoting comprehensive risk management to contractors, suppliers, and business partners, to assure the achievement of PTTEP’s vision, mission, strategy and business objectives.
Enterprise Risk Management Framework
Our risk management process is developed based on ISO Standard 31000:2018. and consists of 6 key steps as shown below. The process are scalable – It can be applied at most levels within an organization.
PTTEP aims to integrate risk management into its business activities and decision-making which cover core business activities including products and services of PTTEP such as strategic planning management, investment and divestment decision-making, capital project management, operations and business process management including business continuity management, and ESG management. In addition, the Company implements risk management both in the corporate level and operational level to ensure that all key risks are managed in accordance with risk appetite, allocates necessary resources for managing risk in proportion to the level of risk and cost benefit consideration, and monitors the progress of risk mitigation plans together with Key Risk Indicators (KRIs) which serve as a tool for early warning for timely executing prevention activities and properly setting up additional mitigation measures.
Risk Management Process
1. Scope, Context, Criteria
PTTEP provides a foundation for understanding how risks may impact our operations and guides subsequent risk management activities. Establishing the scope, the context and criteria is the process to define the objectives and understand the external and internal business context. A common understanding of these points is the key to success in risk management.
2. Risk Assessment
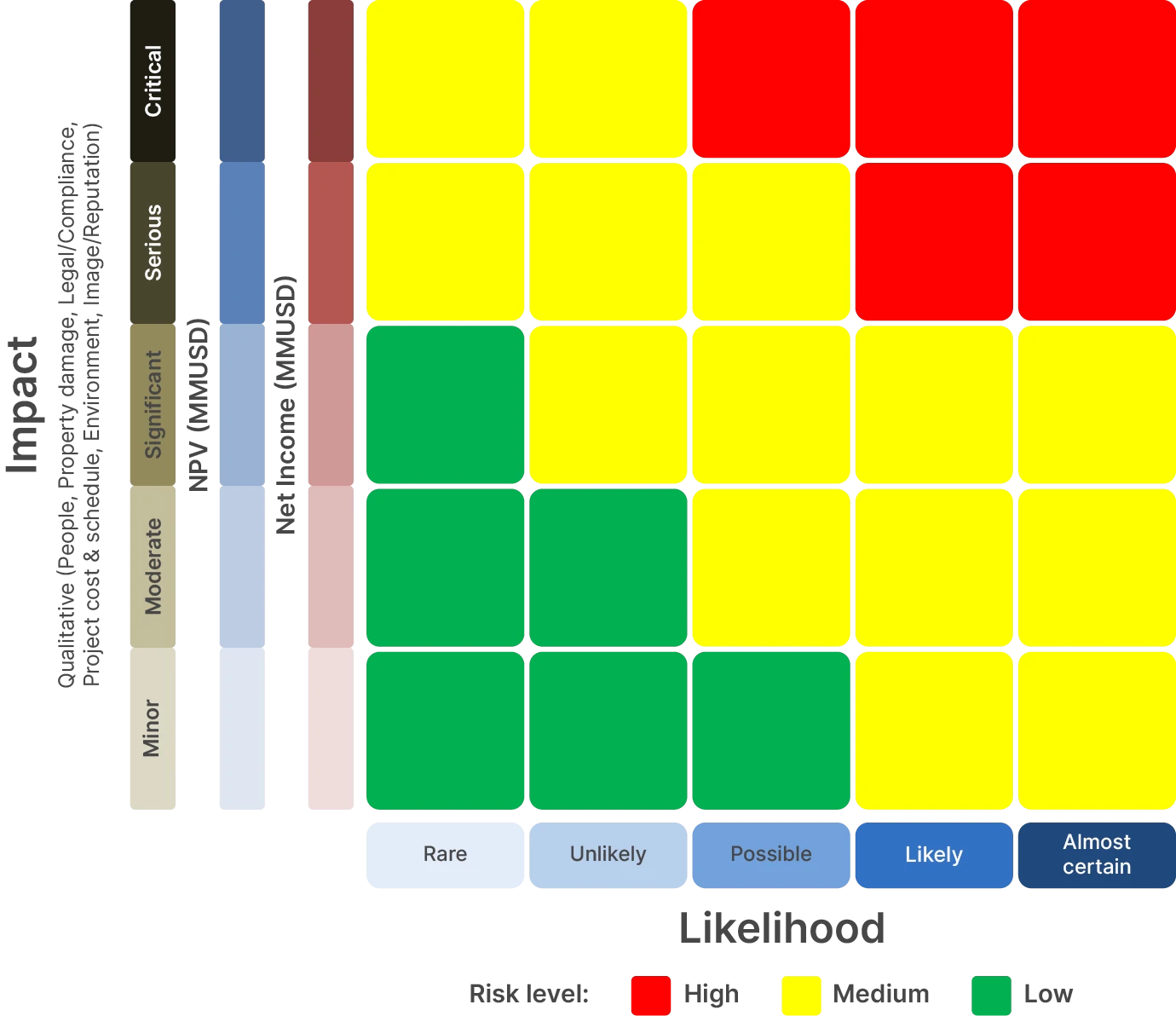
PTTEP conducts comprehensive risk assessments covering Strategic & Portfolio Risks, Financial & Market Risks, Political and Legal/Regulatory Risks, Operational Risks, and Emerging Risks. We evaluate the levels of identified risks using criteria based on impact and likelihood:
Risk Rating Scale
PTTEP establishes common rating scales for two dimensions which are impact and likelihood to align understandings among relevant parties regarding how to measure as per the rating scales.
- Likelihood criteria : Llikelihood of some kind of risks is rated based on comparable occurrence to normal situation or experiences of risk owner. The degree of likelihood is subjective and possibly not in line with frequency probability but make sense in term of risk management. The 5-rating scale below provide brief criteria scale of likelihood.
- Almost certain (5) : Event has occurred frequently in E&P industry OR occurred more than once per year at the same location OR is expected to occur in PTTEP.
- Likely (4) : Event has occurred several times per year in the E&P industry OR more than once per year in PTTEP OR occurred at the same location OR is likely to occur in PTTEP
- Possible (3) : Event has occurred several times in the E&P industry OR occurred once in PTTEP OR may occur in PTTEP
- Unlikely (2) : Event has occurred few times in the E&P industry OR is unlikely to occur in PTTEP
- Rare (1) : Event occurrence is remote and/ or never heard of in the E&P industry
- Impact category : PTTEP identifies 7 key categories of impact with 5-point rating scale to examine a level of severity. Impact is categorized as 1) Net Income/Net Present Value/Expected Monetary Value 2) People 3) Property damage 4) Project cost & schedule 5) Legal and compliance 6) Environment and 7) Image and reputation.
3. Risk Treatment
The process of risk treatment is developed to Take, Treat, Transfer and Terminate, in line with our risk appetite and tolerance levels.
4. Monitoring and Review
PTTEP continues monitoring risks and mitigation measures which are integral to our risk management process, ensuring that we remain vigilant to changing circumstances and adapt our strategies accordingly. In addition, we also review the risk exposure at least on a quarterly basis. This emphasis on agility allows PTTEP to promptly adjust its responses to incorporate newly identified risks with significant impacts, ensuring we are well-prepared to address risk in a timely, reasonable, and efficient manner.
Moreover, PTTEP conducts both internal audit and external assessment. From the last three years, Internal audit focused on Risk Management Process. In addition, PTTEP engaged independent expert to conduct ERM Maturity Assessment in line several global standards, including ISO31000 and COSO. The scope of the assessment covers Governance & Framework, Process, Culture, and Special Topics such as 3rd-party & partnership risk management. Risk Management Tool and Software and Business Continuity Management The maturity assessment results mostly range from Level 3 (Established) to Level 4 (Embedded).
5. Communication and Consultation
PTTEP ensures all employees are informed, engaged, and empowered to contribute to the success of the risk management program.
6. Recording and reporting
The risk management process and its outcomes shall be documented and reported through risk register tool and system. Risk report supports management and committee in meeting their responsibilities by ensuring that concerned parties can make decision, manage risks effectively and efficiently. Handling the sensitive risk information should be taken into account, but not be limited to their use.
Risk Management Structure
To ensure all key risks are thoroughly and completely identified and effectively managed in accordance with the Three Lines Model, the risk management unit advises and works with the First Line Roles, which carry out their duties and concurrently manage risks as risk owners. The risk management unit also coordinates with other functions especially the Second Line Roles, which support risk management assistance in their own areas of expertise. One of them is a compliance unit which shall monitor regulatory changes that may cause new risks or change risk levels. The internal audit unit, in accordance with the Third Line Roles which is made up of audit functional unit and external auditors, is responsible for independently auditing the overall performance of various management systems under the First and Second Line Roles. This includes ensuring effective and efficient implementation of risk management and providing recommendations for continuous improvement. Furthermore, the risk management unit and the internal audit unit shall exchange information to ensure that key risks are identified and managed continually.
Strategic Risk, Corporate Risk and Emerging Risk
PTTEP integrates strategic risk management into the strategic planning process. This involves assessing strategies from a risk perspective to support the selection of strategies that align with and drive the achievement of the company’s objectives within an acceptable risk level. Strategic risk management also encompasses the ongoing monitoring and reporting of key strategic assumptions, as well as the progress of relevant situations, to evaluate whether the implemented strategies remain viable in a dynamic environment. Furthermore, the Risk Management Department closely monitors emerging situations that may affect the organization’s strategies and provides quarterly reporting to the management and relevant committees. This enables timely review, adjustment, or revision of strategies in response to changing circumstances.
In the process of corporate risk management, PTTEP considers both internal and external contexts that affect the achievement of the Company’s objectives and strategies and may cause risks with high impact at the corporate level, such as significant global events, audit findings, and Risk Management Committee and management concerns. Meanwhile, key risks that are identified and assessed by risk owners will be simultaneously considered to escalate with corporate criteria. All Corporate Risks will be consolidated to formulate our Corporate Risk Profile (CRP) for monitoring and reporting to the management, Management Committee (MC) and Risk Management Committee (RMC). If there is any significant change, it will be promptly alerted to all relevant committees for managing risks in a timely manner. In addition, emerging risks with potential impacts on future business operations are regularly monitored and reported.
PTTEP has successfully implemented and benefited from the web-based Risk Register System (RR System). The system enables risk owners to quickly identify and analyze risks and enhance risk information communication throughout the organization. It also helps the Company to easily consolidate and escalate key risks to Corporate Risks. In 2024, the Company enhanced the Risk Register system by introducing a strategic risk module, perspective on risks beyond those arising from work plan implementation. This improvement has enabled the Company to effectively manage risks and avoid any major issues (No Surprise Problems) due to unregistered risks and to allow all relevant parties to monitor the risk management anywhere and anytime promptly and conveniently. In addition, PTTEP continues to strive for more efficient and faster risk management including developing a Chat Bot to suggest risks and to search for complete risk information leads to manage risks that may arise as a problem and thus will affect the organization's goals.
In 2024, we leveraged a risk matrix to assess key threats to our organization. This matrix considered both the likelihood of a risk occurring and the potential impact it could have. Based on this analysis, we identified mitigation actions to ensure each risk falls within our acceptable risk tolerance level. Furthermore, this example demonstrates our ongoing commitment to proactive risk management through this cyclical process.
| Key Risk and Prioritization | Description | Risk Appetite & Tolerance | Risk Mitigating Actions (Current Control) |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Strategic & Portfolio Risks: New Investment Risks Prioritization (Likelihood and Impact): HIGH |
PTTEP aims to maintain reserves-to-production ratio by seeking new business opportunities with strategic partners. Core areas include Thailand, Myanmar and Malaysia and the Middle East, considering factors like petroleum potential, project characteristics, political stability, and economic conditions. |
PTTEP accepts investment risks in oil and gas exploration, recognizing them as part of our core business. We also invest in businesses aligned with our strategies, balancing risks with potential returns and benefits for stakeholders. The example of Risk metrics and Limits aligned with Risk Appetite are set.
|
PTTEP has established a risk management process to assess each investment in various aspects, ranging from petroleum potential, size and project characteristics, acquisition procedures, additional reserves, operator’s capability and performance, attractiveness of the fiscal regime, geographical conditions, related laws and regulations, political stability, issues concerning international relations, and economic and financial stability. Moreover, the Company also seeks advice from consultants who have expertise in such countries. Risk management measures are determined in advance of the selection of projects. Such risks are then integrated into a return-on-investment analysis or a sales and purchase agreement/ joint venture agreement. Moreover, PTTEP considers new investments that align with the Net Zero Greenhouse Gas Emissions target, with a focus on natural gas investments, where greenhouse gas intensity is taken into account in the decision-making process. Projects are screened by the Investment Committee, Management Committee, Risk Management Committee endorsement prior to Board of Directors’ approval. |
|
Operational Risk: Exploration Risks Prioritization (Likelihood and Impact): HIGH |
Exploring new petroleum sources is vital to PTTEP's growth. Risks include geological risks and resource volume uncertainty. Key factors affecting decisions are success chances, resource estimation, costs, and contract terms. |
PTTEP accepts investment risks in oil and gas exploration, recognizing them as part of our core business. We also invest in businesses aligned with our strategies, balancing risks with potential returns and benefits for stakeholders. The example of Risk metrics and Limits aligned with Risk Appetite are set.
|
PTTEP employs a clear and systematic approach to exploration and production (E&P) project evaluation, ensuring that each phase of the E&P lifecycle is underlined by clear processes, guidelines, and criteria to maximize exploration success and minimize risks. The approach comprises potential petroleum basin evaluation and selection, in-depth subsurface studies of targeted blocks, and above-ground investment risk analysis. The Geosciences, Subsurface, and Exploration Group of PTTEP evaluates the global target areas to identify those with the highest potential for selection in bidding or joint venture opportunities. Once projects are secured, the group plans short-term and long-term exploration activities within the exploration budget set by the Company. PTTEP’s exploration strategies are reviewed and refined annually. These processes are reviewed annually, with target areas and exploration strategies adjusted to align with the results of previous exploration activities. In addition, PTTEP has established a Technical Assurance Committee as an additional layer of review and oversight in the exploration preparation process. This ensures that key technical aspects are thoroughly analyzed and that exploration assessments align with PTTEP’s internal standards and guidelines, supporting well-informed investment decisions that contribute to both current and future production targets. |
With the current situations, such as changes in business environment and advanced technology as well as the rising of stakeholder expectations regarding the Company’s regulations compliance and more intensive environmental impact mitigation measures, PTTEP, therefore, keeps monitoring situations and assessing emerging risks that may affect the Company’s business operations in the future and report to the management and relevant committees in order to follow up and update risk mitigation plans as well as to adjust corporate strategy efficiently. These would also enhance our competitiveness and create an opportunity to continue our business with sustainable growth.
Based on the enterprise risk factors, PTTEP has identified emerging risks. Hence, the prioritization of these emerging risks is based on the existing risk factors. Currently, PTTEP has identified and keeps monitoring emerging risks as follows.
1. Risk from Extreme Weather Events
Extreme weather events, such as heatwaves, heavy rainfall, tropical cyclones, droughts, and water resource-related challenges, are increasingly becoming significant risks due to their growing frequency, intensity, and unpredictability. This trend, driven by global climate change, introduces cascading challenges that extend beyond immediate operational disruptions to long-term systemic impacts on infrastructure, supply chains, and financial stability.
- Timeframe: 3-10 years
- Risk category: Environmental
- Prioritization (Likelihood and Impact): MEDIUM
Scenario and Impact to PTTEP:
PTTEP identifies extreme weather events as an emerging risk due to their rapid escalation in frequency, intensity, and unpredictability. These events pose challenges and systemic impacts driven by global climate change, requiring the adoption of new models, tools, and collaborative approaches for effective mitigation. This highlights the importance of integrating climate resilience and adaptive strategies into the PTTEP’s broader risk management framework.
The intensifying effects of climate change pose critical challenges to operational stability, asset integrity, financial performance, and supply chain management. These challenges manifest in several key areas:
-
Operational disruptions: The increasing severity and unpredictability of extreme weather events, such as tropical cyclones and heavy rainfall, could disrupt onshore and offshore operations in key regions, including Thailand, Malaysia (Sabah and Sarawak), and Myanmar. Additionally, prolonged heatwaves and droughts may reduce water availability, a critical resource for operational processes, further exacerbating risks to stable operations.
-
Asset integrity and safety: Extreme weather conditions subject infrastructure to substantial physical stress, threatening infrastructure’s integrity, for example, cyclones, heavy rainfall, and other adverse conditions can weaken infrastructure over time. Furthermore, workplace safety is at risk during extreme climate events, underscoring the need for comprehensive employee protection measures. To address these challenges, PTTEP requires significant resource allocation toward advanced monitoring systems, infrastructure upgrades, and emergency response mechanisms.
-
Financial impacts: The financial implications of climate change are significant. Increased expenditures on repairing and maintaining infrastructure to withstand heightened extreme weather risks are inevitable. Moreover, downtime or reduced operational capacity during adverse conditions can result in revenue losses.
-
Supply Chain Disruptions: Extreme weather events can severely disrupt supply chain continuity, especially when critical materials or services are locally sourced from affected regions. These disruptions can cascade across operations, impacting production schedules and delivery timelines.
These impacts underscore the need for PTTEP to adapt the strategy and business model to remain resilient in the face of extreme weather events while capitalizing on opportunities for innovation and sustainability.
Mitigation plan:
PTTEP develops and implements a Climate Management Plan to proactively address the risks posed by extreme weather events, ensuring personnel safety, the assets’ protection, and operational continuity. This plan integrates a multifaceted approach, combining advanced technology, strategic infrastructure adaptations, robust risk management practices, and collaborative efforts with stakeholders to enhance resilience across all aspects of PTTEP’s business. The plan focuses on both short-term preparedness and long-term resilience through infrastructure upgrades, climate adaptation strategies, and sustainable resource management. Key mitigation plans include:
- Infrastructure Resilience: Conduct regular site monitoring and inspections, considering incorporating climate scenarios into the design phase for new projects, and performing site-specific risk assessments to refine predictive models for weather patterns and their operational impacts.
- Emergency Preparedness, Response, and Recovery: Developing proactive resource pre-positioning plans and streamlined recovery processes, implementing safety systems to remotely and automatically secure facilities during severe weather, leveraging insurance as a financial tool to support resilience and recovery efforts, and establishing Business Continuity Plans (BCPs) to maintain critical operations with minimal disruption.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Collaborating with governments, insurers, local communities, and relevant organizations to strengthen disaster preparedness and response efforts.
These measures are part of PTTEP's broader approach to maintaining resilience against extreme weather events while leveraging opportunities for adaptation and long-term sustainability.
2. Flawed Decisions from AI Misinterpretation
Utilizing AI technology in organizations to enhance operational efficiency, while presenting new opportunities, also introduces new risks that organizations must adequately address. This is particularly crucial in the Oil & Gas industry, characterized by its complexity and demand for high data accuracy. PTTEP acknowledges these risks and has implemented AI risk management to continuously monitor, establish preventative measures, respond to, and mitigate these risks. The primary risks associated with AI usage are as follows:
- Timeframe: 3-10 years
- Risk category: Technology.
- Prioritization (Likelihood and Impact): Medium
Scenario and Impact to PTTEP:
- Data Security Risks: Similar to general cyber threats, AI usage increases the possibility of novel cyberattacks, such as direct attacks on AI models (Model Poisoning, Adversarial Attacks) or utilizing AI to attack other systems. PTTEP prioritizes the security of data used for AI training and the resulting AI output. Comprehensive preventative measures are in place, ranging from access control and data encryption to verifying the accuracy of data input into AI models. 24/7 cyber threat monitoring is conducted through the Cyber Security Operation Center (CSOC), connected to the Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) system.
- Credibility and Accuracy Risks: AI can generate content that appears credible but is inaccurate, potentially leading to flawed decision-making. PTTEP emphasizes rigorous verification of the data used for AI training and the resulting output. The PTTEP AI Platform serves as the central platform for controlling and managing AI models, from data retrieval and training to monitoring and evaluating model quality. Guidelines for human-AI collaboration (Human Oversight) are also established to ensure human involvement in verifying and validating AI results before practical application.
- Data Privacy Risks: AI usage may involve processing personal data which relates to laws and regulations. PTTEP has established a comprehensive Data Governance framework encompassing data access, quality control, and privacy protection to ensure AI usage complies with all applicable regulations and laws.
- Bias Risks: AI can learn and reflect biases present in training data, potentially leading to unfair outcomes. PTTEP is collaborating with consultants to develop policies and guidelines for ethical and responsible AI usage to mitigate bias risks and promote fairness in AI applications.
- Human-AI Collaboration Risks: Collaboration between humans and AI can lead to misunderstandings or communication errors. PTTEP focuses on fostering understanding and developing necessary skills through training programs for working with AI. Clear roles and responsibilities are to be defined for human-AI collaboration.
- Operational Risks: Risks from inappropriate decisions based on incorrect AI recommendations can impact various operational processes. PTTEP emphasizes the importance of Human Oversight, ensuring human involvement in reviewing and validating AI recommendations before implementation. Collaboration guidelines (Human Oversight) are defined to ensure a significant human role in supervision and final decision-making.
- Revenue Loss Risk: Incorrect AI decisions can lead to revenue or profit loss. PTTEP prioritizes careful evaluation of the impact of AI usage. AI models are tested and evaluated in simulated real-world data before deployment. Continuous monitoring and evaluation of AI performance are conducted through the PTTEP AI Platform.
Mitigation plan:
PTTEP has initiated monitoring of these AI-related risks to ensure the organization can effectively control situations and respond to risks arising from AI usage.
Risk Culture
PTTEP is committed to promote risk management as an integral part of the corporate culture by fostering risk awareness among all PTTEP personnel together with competency development via training courses and various activities. The management at all levels are determined to serve as leaders and role models, as well as promoting the implementation of risk management as a corporate culture. In addition, the management also supports employees on regular reviews and improvement of risk management by applying lessons learned and knowledge management for continual development of efficient and effective risk management. Risk coordinators are assigned to each business unit and project both domestic and international to work in coordination with risk owners and risk management units to drive the implementation of risk assessment and management throughout the organisation.
Throughout 2024, PTTEP had continued its communication campaigns to foster an understanding of risk management and business continuity management for all employees in the organisation through training courses and workshops. The GRC is in You Roadshow activities were organised at the headquarters and across various domestic and international locations including in Myanmar and Malaysia, engaging employees working in both offshore and onshore premises. Various online media channels, such as the series of the podcast “Low-Risk High Return”, poster and E-Learning materials together with live broadcast channel were utilised to share important information on issues such as the background of the Overlapping Claims Area (OCA) issue, to increase employees’ awareness of the current global issues that may be the cause of risks to the Company
Focused Risk Management Training and Capacity Building
All Levels
PTTEP has implemented training programs focused on risk management principles and risk assessment. For example, Risk Management Concept and Risk Register Training to Risk Coordinators, Risk Management Concept (Risk VS. Look Like Risk) Training to all staffs, Risk Management Workshop to Malaysia asset relevant management and working team, etc.
On one hand, PTTEP also ties financial incentives to risk management goals to build a strong culture of risk awareness among senior, line managers or relevant personnel. We set specific key performance indicators (KPIs) such as related completion of SSHE plans, deployment of GRC (Governance, Risk management and Compliance) plans that directly impact pay and evaluations. This creates a unified culture focused on risk awareness and continuous improvement
Board Level
Furthermore, our non-executive directors possess experience in Enterprise Risk Management, and we conduct regular risk management education sessions for them. These sessions are designed to enhance their understanding and expertise in enterprise risk management.
Regular Risk Management Education for Directors
| Risk Management | List of Directors Attended |
|---|---|
|
Risk training during board level risk management committee orientation comprising general risk management process
|
All non-executive, executive and independent directors are required to attend. In 2024:
|
|
Specific training
|
|
|
Regular Risk Management Education
|
|
Business Continuity Management (BCM)
PTTEP has developed a Business Continuity Management System (BCMS) which is part of the enterprise risk management. A business continuity framework and the Business Continuity Management Policy have been issued in accordance with the international standard for business continuity management ISO 22301:2019 with the following objectives:
- 1 To build the organization’s capability to be resilient and develop a Business Continuity Plan (BCP) to prepare the Company to operate under emergency or crisis situations.
- 2 To protect our people, organization, brand and reputation, the interests of our stakeholders and the wider community.
- 3 To mitigate the risks of disruptive incidents, ensure mitigation, strategy & solution in accordance with PTTEP policies.
- 4 To minimize risks of non-compliance with government regulations and laws including any contract or agreement with our partners, customers, suppliers and contractors.
- 5 To continuously improve the organization’s business continuity capabilities.
The Business Continuity Plan (BCP) is regularly reviewed and exercised to ensure relevance and that those involved are able to apply the plan in an accurate and timely manner.
PTTEP has developed a Business Continuity Management System (BCMS) which is part of the enterprise risk management. A business continuity framework has been developed in accordance with the international standard for business continuity management ISO 22301:2019 to build the organization’s capability to be resilient and to develop a Business Continuity Plan (BCP) to prepare the Company to operate under emergency or crisis situations. The Business Continuity Plan (BCP) is regularly reviewed and exercised to ensure relevance and that those involved are able to apply the plan in an accurate and timely manner. Since 2023, PTTEP has strengthened our BCMS by centralizing it through the establishment of PTTEP ONE BCMS, which is certified by the British Standards Institution (BSI). In 2024, we began leveraging the BCMS Digital Platform to further enhance our business continuity management capabilities.