Safety, Security, Health and Environment
Importance and Mission
At PTTEP, Safety, Security, Health and Environment (SSHE) is one of our business principles with the aspiration of achieving zero incident organization (Target Zero). A proactive safety culture has been instilled, and emphasis is placed on the personal safety of all workforce and the process safety of our facilities. The Company implements the SSHE Management System that is in line with our SSHE policy and complies with international standards and industry best practices to ensure that everyone working with the Company returns home safely and that incidents are prevented to avoid causing impacts on stakeholders and the environment.
Vision
Zero Incident Organization
Mission
- 1 Prevent all incidents through proactive personal and process safety management.
- 2 Embed SSHE mindset and leadership at all levels toward a generative SSHE culture.
- 3 Recognize SSHE as a foundation towards competitive performance and innovation for long term stakeholders value creation.
Goals
- 1 Achieve zero incidents (Target Zero)
- 2 Maintain personal safety of all employees and contractors and process safety of all facilities
Management Approach
Oversight
PTTEP SSHE Council Member reviews the SSHE performance on a quarterly basis to ensure its effective implementation across the organization. The SSHE Council, chaired by the Chief Executive Officer (CEO) and composed of all Executive Vice Presidents and selected Senior Vice Presidents responsible for operations and related support functions, meets at least quarterly. The SSHE Council has primary responsibilities that include endorsing SSHE policies and strategies to align with PTTEP growth objectives and the PTT Group, ensuring their effective execution, providing necessary resources such as financial support, manpower, and technology for policy implementation, and conducting regular performance reviews to foster continuous improvement and achieve operational excellence in SSHE. Any critical issues from the SSHE Council will be escalated to the Board of Director by the CEO, who is the member of the Board of Director, and vice versa.
Safety, Security, Health and Environment Policy (SSHE)
SSHE is fundamental for PTTEP's business. To achieve and sustain excellent performance toward relevant Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), we put in place and adhere to an effective SSHE management system in order to ensure the safety and health of everyone involved in our operations and communities where we operate, environmental protection and the security of our people and assets.
To achieve our vision of being a zero incident organization, PTTEP shall:
- Strive for a generative SSHE culture through accountable leadership and involvement of all employees and contractors.
- Set measurable objectives, KPIs, targets, and action plans to deliver top–quartile SSHE performance, which is a line management accountability.
- Fulfil compliance obligations with applicable SSHE laws, regulations, internal requirements, and national and international standards.
- Manage SSHE risks to As Low As Reasonably Practicable (ALARP) throughout the PTTEP business lifecycle and when Management of Change (MOC) is applied.
- Promote an effective health management system and enforce zero drugs and alcohol programs in the workplace.
- Reduce environmental footprints in alignment with low carbon pathway, circularity concept, and positive Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services (BES) value creation.
- Protect all employees and the organization from pandemics, natural disasters, security threats, and vulnerabilities by effectively managing emergencies, crises, and business continuity.
- Empower everyone to exercise Stop Work Authority (SWA).
- Commit to continuous SSHE performance improvement via regular training, stakeholder participation programs, and upgrading systems and tools with technology.
The successful implementation of this policy requires total commitment from PTTEP employees and contractors at all levels by being mindful in every action.
(Remarks: PTTEP SSHE Policy is annually reviewed by the SSHE Council and approved by the Chief Executive Officer (CEO), the Director and Secretary to the Board of Directors )Safety, Security, Health and Environment Management System (SSHE MS)
PTTEP's SSHE Management System (SSHE MS) is an integration of the Company's safety, security, health, and environmental policies, vision, and corporate strategy, to mitigate risks induced by the Company's internal operations. The focus is on ensuring a safe work environment and prevention of work–related incidents, injuries and illnesses, as well as environmental impacts. The SSHE MS is also aligned with the International Association of Oil & Gas Producers (IOGP)'s guidelines as well as international standards like ISO 14001:2015 Environmental management System and ISO 45001:2018 Occupational Health and Safety Management System.
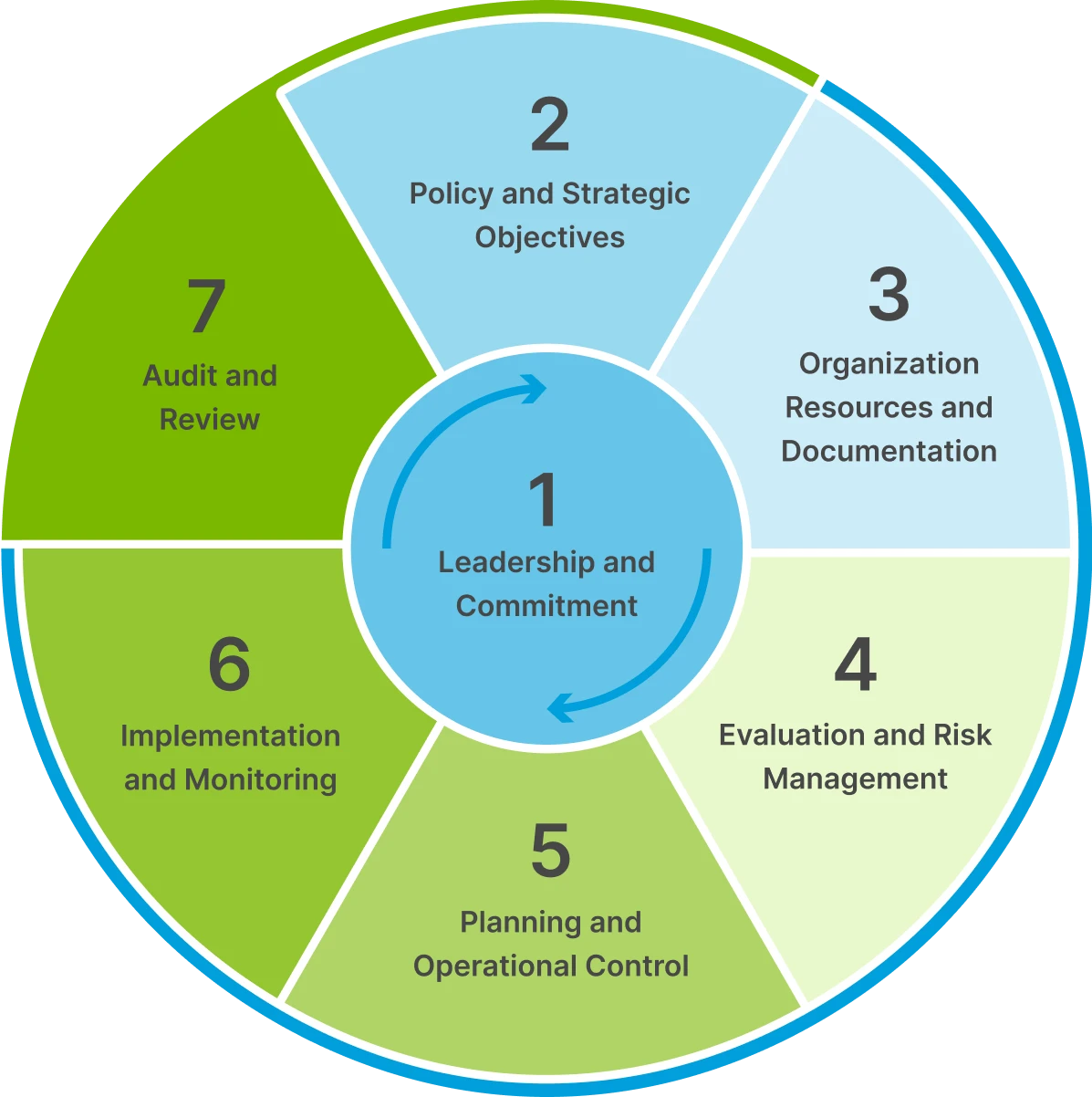
PTTEP's SSHE MS comprises of seven elements:
| SSHE Element | Addressing |
|---|---|
| 1. Leadership and Commitment | Top–down commitment and SSHE culture, essential to the success of the SSHE MS |
| 2. Policy and Strategic Objective | Corporate intentions, principles of action and aspirations with respect to SSHE |
| 3. Organization Resource and Documentation | Organization of people, resources and documentation for sound SSHE performance |
| 4. Evaluation and Risk Management | Identification and evaluation of SSHE risks, for activities, products and services, and development of risk reduction measures |
| 5. Planning and Operational Control | Planning the conduct of work activities, including planning for changes and emergency response |
| 6. Implementation and Monitoring | Performance and monitoring of activities, and how corrective action is to be taken when necessary |
| 7. Audit and Review | Periodic assessments of SSHE MS performance, effectiveness and fundamental suitability |
PTTEP has implemented a comprehensive annual SSHE Management System (MS) internal audit plan to systematically evaluate the effectiveness of SSHE MS implementation across the organization. Each year, these internal audits were successfully conducted, encompassing 100% of operations and operations support activities. Additionally, the company underwent ISO attestation, external audits, and certifications in compliance with internationally recognized standards, including ISO 14001:2015 and ISO 45001:2018. These external assessments were strategically designed to cover a wide range of the company's operational activities, ensuring adherence to global best practices in safety, security, health, and environmental management. The extent of such external assessment is as follows:
ISO 14001:2015 and ISO 45001:2018 Attestation
- PTT Exploration and Production Public Company Limited: all operating assets where PTTEP has control as the operator.
ISO 14001:2015 Certification for Environmental Management System
- International Asset: Zawtika and Yadana Project in Myanmar, Project in Malaysia (Located in Sabah and Sarawak)
- Petroleum Development Support Bases: Songkhla and Ranong Bases
ISO 45001:2018 Certification for Occupational Health and Safety Management
- Petroleum Development Support Bases: Songkhla and Ranong Bases
SSHE Culture Management
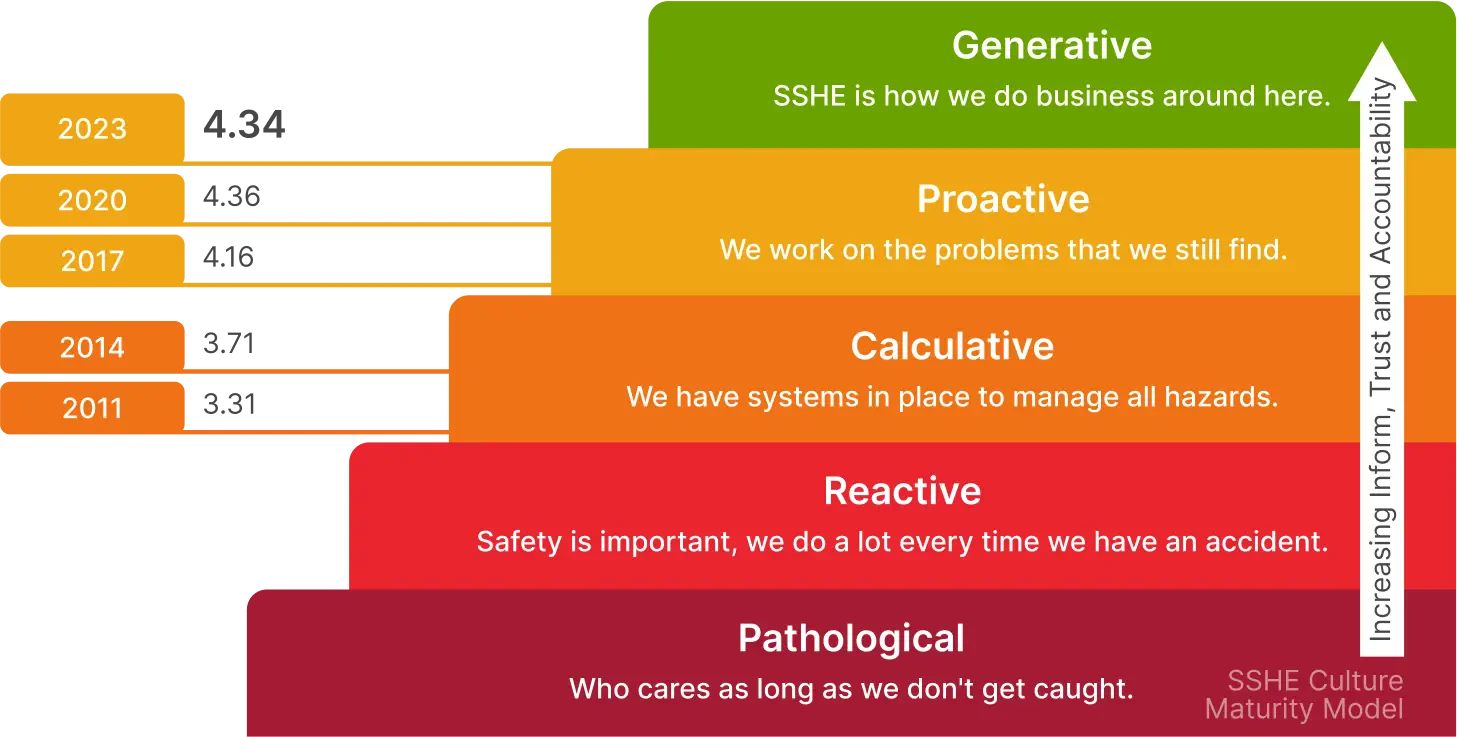
SSHE Culture development is essential for enhancing the SSHE performance of the organization. Since 2011, PTTEP has adopted the SSHE Culture improvement model based on the HSE Culture Ladder Model from the Energy Institute (EI), which identifies five levels of HSE culture, ranging from Pathological to Proactive.
The SSHE culture survey is conducted every three (3) years. Regarding the first SSHE culture survey in 2011, PTTEP’s SSHE Culture Maturity level was 3.31 (Calculative level). As a result, the SSHE culture improvement plan was developed and implemented. In 2017, continuous improvement was demonstrated from the survey results, in which the SSHE Culture Maturity Level for PTTEP reached 4.16 (Proactive level) from the highest at 5.
The SSHE culture maturity level of the entire organization increased to 4.34 (Proactive level) based on the 2023 SSHE culture survey results, with no distinction between the results of top management and employees. Regardless of position, all PTTEP employees have the same level of SSHE awareness. In addition, mode 1 contractors were initially engaged in the SSHE culture survey in 2020. PTTEP expanded the scope of the SSHE culture improvement and development technique in 2022 to include mode 2 contractors performing high-risk activities, as detailed in the contractor safety topic.
PTTEP establishes a 3-year plan (2024-2026 SSHE Culture Improvement Plan) to strengthen its SSHE culture. Continuous monitoring is conducted periodically to ensure the improvement of the SSHE culture maturity level in all operating areas and the achievement of the objective of becoming an incident-free organization (Target Zero). The following SSHE culture survey is planned for 2026.
Embedding SSHE Culture
All PTTEP operations are instilled with a strong SSHE culture, which contributes to our improved safety performance as we strive to become a Target Zero organization. Even though incidents continue to occur, the Company remains fully committed to strengthening the SSHE culture, particularly emphasizing personnel safety and SSHE leadership. Moreover, the development of tools to support the PTTEP SSHE Leadership Program is underlined. This program was expanded to include frontline supervisors, i.e., PTTEP employees and contractors, through various trainings in the previous year.
As a robust SSHE culture begins with competent workforces, the Company identifies training needs on SSHE for employees and contractors in accordance with its SSHE Training and Competency Standard and provides them with the basic knowledge and skills required for their assignments. In 2024, 131 SSHE training classes were delivered to employees, which comprised 27 on-site and 104 e-learning classes. In total, there were 18,395 participants attended the training including the Basic SSHE Awareness course as a compulsory program designed to ensure all employees have the foundational knowledge to uphold SSHE standards in their roles.
- SSHE Leadership
- Risk Assessment and Job Safety Analysis
- Contractor Management
- Basic Incident Investigation and Root Cause Analysis
- Safe Lifting Operation
- Process Safety Principle - Management of Major Accident Event (MAE)
- Management Of Change (MOC) Awareness
- Corporate Emergency Management Team
Besides, the Company has continued to improve tools that promote SSHE culture, e.g., an electronic Safety Observation & Communication Card (SOC), Hazard Reporting Card (HRC), and Operational Control Verification Program. These tools primarily focus on workplace safety and increasing the observation and detection of unsafe behaviors and unsafe working conditions, with the aim of eliminating and/or reducing risks. PTTEP empowers all its employees and contractors to "Stop Work" when unsafe conditions or behavior is detected.
Emergency and Crisis Management
PTTEP recognizes that the petroleum exploration and production business requires high standards of safety. As such, PTTEP developed Emergency and Crisis Management Plans under the framework of the SSHE MS. The plans clearly outline a systematic structure to ensure the Company's readiness for emergency and crisis situations and their probable consequences to ensure the mitigation and recovery actions are put in place to reduce risk to the acceptable level, and giving priority to the protection of human lives, the environment, properties, and PTTEP's reputation. Joint exercises between the assets teams and corporate level personnel based on the Emergency and Crisis Management Plans are conducted on a regular basis. Results and feedback from these exercises are communicated to those responsible at the assets and corporate levels. They are used to improve the plans as well as to continuously enhance the competency of responsible personnel to effectively manage all forms of crisis situations.
Personal Safety
PTTEP believes incidents are preventable, to attain "Target Zero". This conviction is communicated repetitively from top management to all employees and contractors. Therefore, PTTEP emphasizes promoting safety culture in every stage of the work process. The Company's SSHE policy and management system were designed to meet relevant international standards, to manage work–related risks and ensure that everyone working with PTTEP returns home safely.
In 2024, the overall SSHE performance statistics in terms of the Lost Time Injury Frequency (LTIF), Total Recordable Injury Rate (TRIR), Loss of Primary Containment Rate (LOPCR), and Spill Rate increased compared to the previous year. The LTIF was equal to the average safety performance of the International Association of Oil & Gas Producers (IOGP), while the TRIR was better than the average safety performance of the IOGP in 2023.
In response to the incidents that occurred in 2024, the Company enhanced its safety oversight of these assets by expediting the closure of SSHE improvement gaps, maintaining close communication, and enforcing stringent measures to prevent recurrence. Additionally, the Company emphasized visible SSHE leadership and launched the Learning from Normal Work (LFNW) campaign to drive continuous improvement in SSHE performance. (Details on the number of personal incidents are shown in Health and Safety Performance Data. )
The investigation results of the incident showed that the main root causes were human factors, risk assessment, and inadequate supervision onsite, including inadequate communication of hazards and risks to workers. Additionally, the total work hours increased to more than 50 million hours in 2024, leading to a lack of competencies and experience among new staff and contractors. Over these two years, incidents have been more prevalent among new staff compared to their more experienced counterparts. PTTEP focuses more on human factors, maintains high SSHE standards, and provides action plans by emphasizing the safety leadership of the frontline supervisors to manage and communicate hazards and risks at the site and promote the SSHE knowledge and competency of the workforce. These are to ensure that employees and contractors will be able to work safely.
PTTEP has established SSHE targets for motor vehicle and marine vessel incidents. To prevent transportation incidents and to ensure that workers will work safely, awareness of transportation incident prevention is promoted for all PTTEP transportation activities, including the Company's and contractors' vehicles and vessels. The Fatigue Management campaign was launched in late 2024 to ensure drivers are adequately prepared and fit for duty. However, no vessel accident was reported for four consecutive years. (Details of the transportation-related accidents are shown in Health and Safety Performance Data. )
PTTEP has integrated contractors into our health and safety management system and continuously improved SSHE contractor management to ensure that all suppliers and contractors can work and return home safely. The Company has established a long history of the annual SSHE Forum that brings together suppliers and contractors to demonstrate PTTEP’s strong commitment to improving SSHE and achieving Target Zero. PTTEP has continued to present an award to contractors with excellent SSHE performance to appreciate and promote their commitment to safety.
PTTEP has a contractor pre-qualification process, where the SSHE capability of the contractor is assessed to ensure that they have the necessary SSHE organization, culture, resources, capability, and management system to undertake the scope of work in a safe, sustainable, and responsible manner. The SSHE training requirements or SSHE Training matrix are incorporated into the contract requirements and audited during the Pre-mobilization. The pre-mobilization kick-off meeting is also conducted for all contractor work crew to reiterate SSHE rules and regulations and to provide Asset SSHE induction training to the contractors.
PTTEP works closely with high-risk contractors and underscores the importance of contractor safety with our contract holders. PTTEP also monitors and evaluates the safety management of contractors on-site to prevent incidents. In addition, PTTEP provides induction training to contractors prior to the commencement of the work. Last year, a survey of contractors on the SSHE culture to establish the work plan for improving and strengthening the SSHE culture to align with PTTEP.
Furthermore, PTTEP provides contractors with guidance on health risk assessment to ensure that their occupational health risk assessment is comparable to ours. The results are communicated to the appropriate parties and support the formulation of a risk mitigation plan to lower risks to an acceptable level. This will improve the health of our employees and contractors. The health risk factors considered include physical, biological, chemical, ergonomic, and psychological hazards.
Process Safety
PTTEP’s mission involves the supply of oil and gas to meet the country’s energy demand. In the production process, oil and gas leaks can cause serious incidents that endanger lives, the environment and assets. Recognizing this potential, PTTEP integrates Process Safety Management into the SSHE Management System (SSHE MS) to prevent and mitigate Major Accident Events in our operations. The Process Safety Management system is based on the Energy Institute's guidelines which are in line with international manufacturing Process Safety Management requirements. It is based on the following four principles:
- Commitment to prevention of Major Accident Events and Process Safety;
- Understanding process hazards and risks;
- Management of process hazards and risks to As Low As Reasonably Practicable (ALARP) throughout the asset development lifecycle;
- Learning and improving from experience.
These principles have been implemented by all relevant units across the organizations, to ensure the safety of all production and drilling equipment in all fronts, namely:
Design Integrity
Maintenance Integrity
Operating Integrity
Well Integrity
The integrity in the four fronts is identified as "safeguard" to prevent and minimize hazards and their consequences. PTTEP has a reporting process in place and requires regular inspection against the required standards and stresses that maintaining process safety is an individual responsibility. Furthermore, PTTEP reported and analyzed leakage-related incident statistics from the production process in order to identify the causes and plan preventive measures. In 2024, PTTEP focused on improving the following processes:
- Improve construction QA/QC including material quality assurance, qualification of contractors performing critical process e.g. welding.
- Ensure construction material compatibility with producing fluid and contaminants characteristic.
- Setup Technical Committee Meeting for each operating asset to monitor Process Safety performance and progress of asset specific LOPC (Loss of Primary Containment) reduction plan.
- Roll out nine Process Safety Rules (Respect hazards, Apply procedures, Sustain barriers, Stay within safety operating window, Maintain safe isolation, Walk the line, Recognize change, Stop if unexpected occurs, Watch for weak signals) which are adopted from IOGP’s Process Safety Fundamentals.
Security
PTTEP has performed Security Risk and Threat Analysis and Assessment in our operation control, which identifies risks and assists in a prevention system and appropriate risk mitigation. In addition, we monitor security-related situations for all our operating sites around the world in order to promptly apply corresponding security measures to manage such risks to our personnel, stakeholders, and assets.
Occupational Health
The PTTEP medical and occupational health team has developed an E–Health Book system to be a company whose employees are physically and mentally healthy. It is an electronic health database that facilitates employee access to individual health records via the company's intranet. The E–Health Book contains employees' annual medical checkups and health risks, allowing the Company to plan health promotion activities and medical checkup programs that are appropriate for each employee and the Company as a whole. The team also conducted Health Risk Assessments (HRAs), and their results are used to enhance existing medical checkup programs pertinent to the employee's assigned work to prevent future health problems. PTTEP sets and tracks progress against targets for Total Recordable Occupational Illness Frequency (TROIF) which includes work–related ill health that results in Fatality (FAT), Lost Time Injury (LTI), Restricted Work Day Case (RWDC) or transfer to another job, and Medical Treatment Case (MTC). This applies to PTTEP operations, Head office, both onshore and offshore, and includes incidents involving employees and contractors.
The primary role of PTTEP's medical and occupational health team is to provide medical and occupational health advice to all employees and contractors. The team is also responsible for developing and maintaining occupational health standards, procedures, and approaches that promote a healthy and hygienic workplace, such as the Wellness Test, Ergonomic Consultation Campaign, and an annual medical and occupational health knowledge session for employees and contractors. (Course details and the number of participants are shown Health and Safety Performance Data. )
PTTEP continues to place the utmost importance on occupational health and safety for workers and associated individuals. In accordance with public health measures, monitoring and preventative measures, such as influenza vaccination, have been implemented to prevent the spread of the virus.
Environment
PTTEP commits to operating business with social and environmental responsibility by adhering to the Safety, Security, Health and Environmental (SSHE) Policy, which integrates the commitment to environmental protection, regulatory compliance, and continuous improvement. Company personnel, business partners as well as contractors working for or on behalf of the Company must implement this SSHE Policy. The summary of PTTEP's Environmental Management appeared in the Company's website; Environment Section , such as