
Sustainability Framework and Long-term Target
Sustainability Journey
PTTEP set sight to be a sustainable organization since its inception in 1985. The journey started with a goal to be a "green organization" to which environment stewardship and management was a priority. The sustainability concept that involves Environmental, Social and Governance elements was subsequently applied and in 2011, PTTEP participated in the United Nations Global Compact (UNGC), demonstrating our commitment to uphold the UNGC 10 principles that highlight 4 main aspects - human rights, labor, environment and anti-corruption. PTTEP has submitted the Communication on Progress to the UNGC annually since 2012 up to the present.
Green Organization
- Emphasis on environmental stewardship and management
- Participate in Thailand Business Council for Sustainable Development (TBCSD) since 1993
ESG Principles
- Apply ESG principles across the organization
- Participate in the United Nations Global Compact (UNGC) since 2011
Outside In
- Align with Global Reporting Initiative Standards: GRI Standards and IPIECA’s Sustainability Reporting Guidance for the Oil and Gas Industry
- Adopt the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals (UN SDGs) and Sustainability Accounting Standards Board's SASB Materiality MapTM for Oil & Gas – Exploration & Production Industry as inputs of materiality assessment for further development of Sustainability Framework and Strategy
- Apply international sustainability assessment criteria such as S&P Global, MSCI, Moody’s, Sustainalytics, FTSE4Good, etc.
Inside Out
- Develop Sustainability Framework and Strategy
- Change PTTEP vision to Energy Partner of Choice
- Announce PTTEP Sustainability Statement as our commitment to conduct our business to ensure sustainability
Best Practice
- Take guidance from the Task Force on Climate-related Disclosures (TCFD) recommendations
- Initiate study and preparations for adopting IFRS Sustainability Disclosure Standards
- Incorporate elements of the Taskforce on Nature-related Financial Disclosures (TNFD) recommendations where applicable
PTTEP’s sustainability reporting aligns with Global Reporting Initiative Standards (GRI Standards) and IPIECA’s Sustainability Reporting Guidance for the Oil and Gas Industry, while also taking guidance from the Task Force on Climate-related Disclosures (TCFD) recommendations and the Taskforce on Nature-related Financial Disclosures (TNFD) recommendations where applicable. Moreover, we are in the process of studying and preparing for the adoption of IFRS Sustainability Disclosure Standards. PTTEP has adopted the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals (UN SDGs) and Sustainability Accounting Standards Board's SASB Materiality MapTM for Oil & Gas – Exploration & Production Industry as inputs for materiality assessment and development of Sustainability Framework and Strategy and several international sustainability assessment criteria, like S&P Global, MSCI, Moody’s, Sustainalytics, FTSE4Good, etc. as part of our sustainability management.
In 2019, PTTEP formulated Sustainability Framework and set clear long-term targets (2030) in alignment with the Company’s key strategies. Under the inside-out approach, PTTEP strived for impressive performance on strong business foundation, to deliver sustainable values to society (From We to World).
In 2020, the Board of Directors made an important step in pushing the organization's sustainability for concrete implementation. The Sustainability Statement was formulated to ensure common understanding among employees and other stakeholders. Moreover, the Corporate Governance and Sustainability Committee is in place to establish policies, targets, and workplans for good corporate governance and business ethics; and sustainability. The committee is also tasked to promote PTTEP’s overall sustainability implementation, including monitoring, evaluating, and disclosing sustainability performance to stakeholders, through committee meetings at least 4 times a year.
Sustainability Statement
PTTEP’s sustainability means being a responsible and resilient organization. We aim to embrace energy transition and create sustainable value to the Company and our stakeholders with commitment to achieving Net Zero Greenhouse Gas Emissions by 2050. Our Sustainability Framework is based on 3 pillars: High Performance Organization (HPO); Governance, Risk Management and Compliance (GRC); and Sustainable Value Creation (SVC).
While growing our business through the gas value chain, we will diversify beyond E&P with focus on technology and innovation, decarbonization, and future energy. Our competitiveness is driven by robust operations and efficiency improvement. We strive to become a GRC role model and zero incident organization. At PTTEP, we operate responsibly to ensure business sustainability with due care for the community, society and the environment.
Approved by PTTEP's Board of Directors on August 19, 2022
Sustainability Framework and Long-term Target
Sustainability Framework
PTTEP has a firm belief that the "Right Balance" of economic, social, and environmental aspects lead to a strong foundation for business sustainability. We have then developed "Sustainability Framework" to steer our business operations. This framework plays a pivotal role in ensuring business continuity to promote energy security while safeguarding both society and the environment. At PTTEP, we recognize the importance of building sustainability from within by fostering strong business performance on a robust business foundation. The goal is to deliver long-term value to all stakeholders while contributing to the sustainability of the society as a whole (From We to World), aligned with our vision to become the “Energy Partner of Choice”.
The Sustainability Framework emphasizes High Performance Organization (HPO), Governance, Risk Management and Compliance (GRC), and Sustainable Value Creation (SVC). The framework supports 17 United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (UN SDGs), focusing on Goals 3, 7, 8, 9, 12, 13, 14, 15 and 16 which are directly related to the Company's strategies, business operations, and long-term targets.

Emphasizing continuous performance improvement to become more effective, efficient, and productive in response to the energy transition with a focus on technology and innovation, decarbonization and future energy.
Emphasizing transparent and efficient operations for the organization's stability and sustainability through governance, appropriate risk management, and internal control as well as strict compliance with relevant laws and regulations.
Emphasizing long-term value creation for all stakeholder groups through organizational sustainability, responsible operations, natural resource conservation, environmental rehabilitation as well as community and social development.
Materiality Assessment Process
PTTEP assessed and reviewed material topics on sustainability including ESG issues based on Double Materiality approach, considering the significance of topics in terms of impact on PTTEP and impact on environment, society (including impacts on human rights) as well as governance and economy, from the perspective of 8 key stakeholder groups: (1) Government Agencies and Regulators (2) Vendors and Contractors/Suppliers (3) Customers (4) Employees and Directors (5) Shareholders and Financial Institutions (6) Business Partners, Consortium and Joint Ventures (7) Communities and Society (8) Press and Media. The material topics were prioritized based on Double Materiality and in line with the Global Reporting Initiative Standards: GRI Standards (2021) and AA1000 AccountAbility Principles Standard: AA1000APS (2018). The material topics reflected national and international sustainability trends corresponding with the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals and Sustainability Accounting Standards Board's SASB Materiality MapTM for Oil & Gas – Exploration & Production Industry. The materiality assessment results served as part of the crucial inputs for shaping and improving corporate strategies. These results were also integrated into the Enterprise Risk Management process, empowering PTTEP to proactively address any risks related to the Company's sustainability material topics. The assessment process can be summarized as follows:
- 1 Understanding the Organization's Context
- Review entire business activities, business relationships, sustainability context, and all stakeholders throughout the value chain.
- Review global trends, conduct peer reviews across the industry and engage with relevant stakeholders to predetermine material issues.
- 2 Identifying Actual and Potential Impacts
- Identify actual and potential impacts of material issues encompassing environment, society (including impacts on human rights) and governance and economy, for both positive and negative impacts as well as opportunities for positive contributions, in the short term and long term, covering all PTTEP's business activities throughout the value chain via conducting an interview session with relevant stakeholders and gathering other perceptions via an online survey.
- 3 Assessing the Significance of the Impacts
Based on the principles of double materiality, the assessment method is shown as follows:
- Engage with external stakeholders to obtain their perceptions on the Company's impacts on environment, society (including impacts on human rights) as well as governance and economy.
- Engage with internal stakeholders (employee group) to obtain their perceptions on sustainability-related impacts on the Company.
- Assess and determine the significance of identified impacts from stakeholder engagement by considering 2 dimensions: 1) severity (scale, scope, irremediability) and 2) likelihood of the impacts.
- 4 Prioritizing the Most Significant Impacts
- Define selection criteria for key material issues.
- Validate key material issues against external professional views covering ESG dimensions. Then, combine the impact score from expert testing with the score obtained from the stakeholders.
- Group interconnected material issues into material topics and submit to the Management Committee for approval and the Corporate Governance and Sustainability Committee for acknowledgement.
- Incorporate material topics as part of the key inputs for shaping and enhancing the Company’s sustainability strategy.
- Gather data on sustainability performance across all material topics for public disclosure through diverse channels to efficiently respond to each stakeholder group. Then, collect feedback and recommendations from relevant stakeholders to improve the efficiency of business operations.
2024 Material Topic
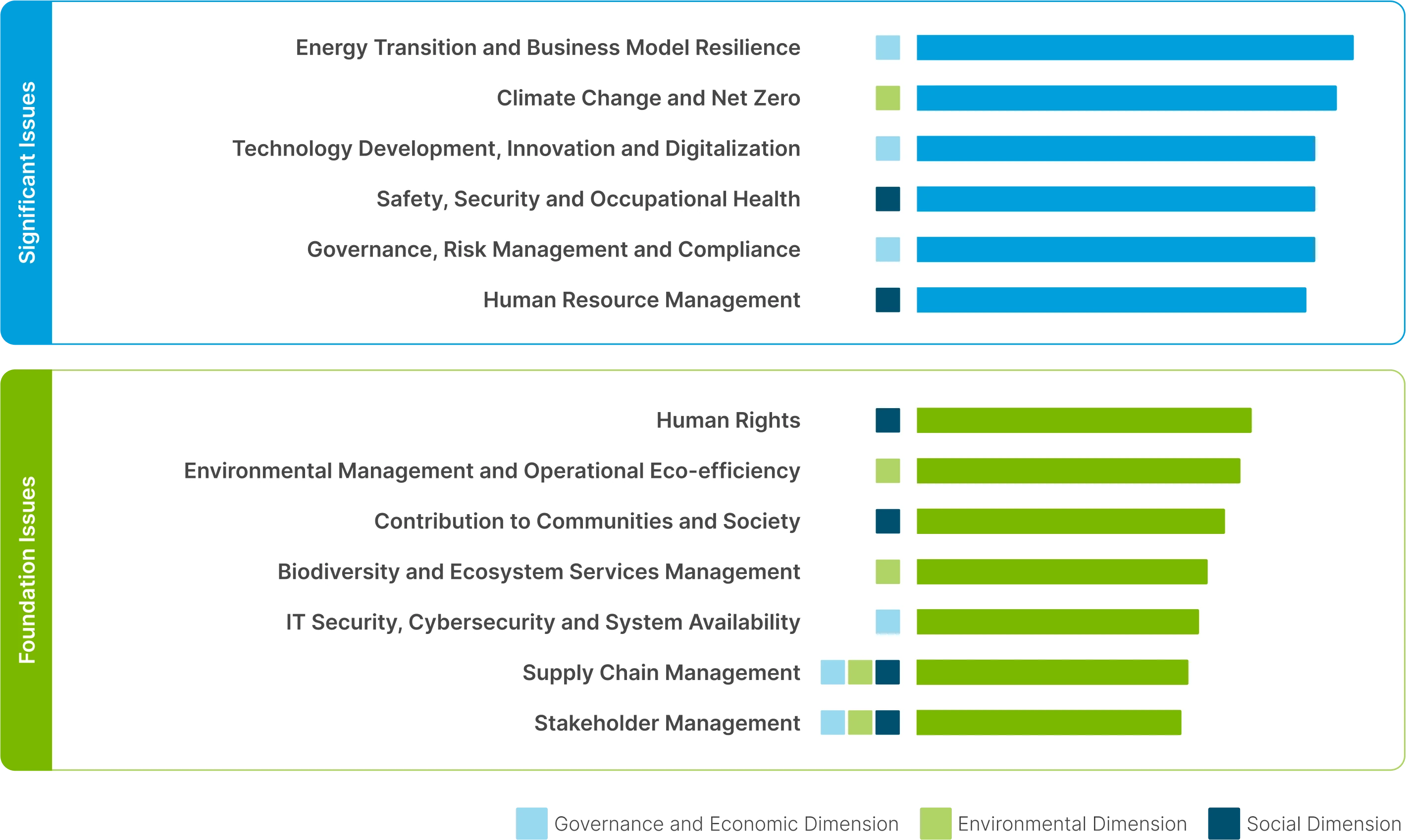
The details of the targets and annual performance summary of material topics can be accessed on PTTEP website under "Performance Summary of Material Topics"
Corporate Strategy and Sustainability Long-term Target
PTTEP is committed to delivering sustainable value from within to support the wider society (From We to World) and supporting the UN SDGs while considering the benefits of all stakeholders involved. Our corporate strategy is formulated with a focus on ensuring energy security and business resilience to address the ongoing global crisis and navigate the energy transition, together with environmental conservation. Therefore, we have established PTTEP Strategy Pillars and sustainability long-term targets encompassing ESG dimensions, with focus on supporting the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals (UN SDGs) as follows:
PTTEP Strategy Pillars
Drive Value
- Strengthen exploration and production (E&P) business and ensure Thailand energy security, supporting domestic natural gas demand in particular
- Maximize natural gas and crude oil production from existing projects
- Expedite development of new projects under development phase
- Accelerate monetization from recent petroleum discovery projects
- Enhance unit cost competitiveness
- Expand gas-weighted portfolio and LNG, especially in upstream and midstream
Decarbonize
- Manage E&P to reach Net Zero Greenhouse Gas (GHG) Emissions target
- Execute GHG emissions reduction plan by leveraging relevant technology application
- Accelerate the development of Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) projects
- Maximize the use of renewables and explore clean future energy application in operational areas
- Study and pursue carbon offsetting preparation through initiatives such as forestation and blue carbon to absorb CO2 in coastal and marine ecosystems under the “Ocean for Life” strategy
Diversify
- Scale up AI and Robotics Ventures (ARV)
- Explore renewable energy opportunities
- Explore the business in relation to Carbon Capture, Utilization and Storage (CCUS), hydrogen and future energy
Sustainability (ESG) Long-term Target and SDGs in Focus
- Pursue sustainable growth in focus areas
- Maintain reserves to production ratio (R/P) to be greater than 5 years
- Maintain competitive unit cost for E&P
- Allocate 10% of PTTEP's total capital expenditure (CAPEX) budget for transition business during 2024-2030
- Achieve Net Zero GHG Emissions by 2050 (Scope 1 and Scope 2) of E&P business under PTTEP's operational control
- Reduce GHG emissions intensity by at least 30% within 2030 and 50% within 2040 (from base year 2020)
- Reduce methane emission intensity to less than 0.2% by 2030
- Reuse at least 50% of main structures, with safety awareness and efficient conditions by 2030
- Achieve zero waste to landfill by 2030
- Achieve Net Positive Impact (NPI) on ocean Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services (BES) value for offshore operations by 2030, compared to base year 2019
- Avoid operation in World Heritage sites as defined by UNESCO
- Maintain no gross deforestation for E&P projects
- Conserve and restore 200,000 rai of forestations by 2030
- Achieve zero oil and chemical spill
- Establish 16,000 conservation networks by 2030
- Achieve zero incidents (Target Zero)
- Achieve stakeholder engagement level at the highest levels as appropriate for each stakeholder group
- Achieve 50% increase in income of focused communities participating in PTTEP projects, compared to baseline data before PTTEP project implementation
- Achieve zero fraud and corruption and zero non-compliance
- Achieve high-impact risk identification with effective mitigation
- Achieve 100% improvement for control deficiency
- Increase GRC maturity level to level 4+ (Transform and Advantaged)
Supporting SDGs
Sustainability Collaboration and Networking

Collaboration and networking play a crucial role for both PTTEP's current business operations and future growth. We, therefore, emphasize the importance of establishing business, social and environmental collaborations and networks with relevant parties to support the Sustainable Development Goals of Thailand and the United Nations; as well as PTTEP's vision of "Energy Partner of Choice".
Elevating Our Standards to a Global Level
PTTEP participates with relevant associations and agencies aiming at driving better economic and societal development by taking a support role. As respectable member in the in oil and gas industry, the Company focuses our contributions on associations and organizations supporting two main objectives: (1) develop and promote responsible practice for oil and gas industry in alignment with global best practice (2) encourage sustainable development in Thailand through partnership with business focusing on the conservation of natural resources and the environment, and business ethics. During 2021 to 2024, PTTEP made monetary contributions to 10 trade associations and tax-exempt groups including:
Network for responsible global practices for oil & gas industry
- International Association of Oil & Gas Producers (IOGP)
- IPIECA - The global oil and gas industry association
- Petroleum Institute of Thailand (PTIT)
- Indonesian Petroleum Association (IPA)
- Oil Spill Response Limited (OSRL)
- Oil Industry Environmental Safety Group Association (IESG)
Collaboration and partnership with business sectors for sustainability
- United Nations Global Compact (UNGC) via Global Compact Network Thailand (GCNT)
- Thailand Business Council for Sustainable Development (TBCSD)
- Malaysian International Chamber of Commerce
- Thai Institute of Directors Association (IOD)
Similar to the PTTEP’s Good Corporate Governance and Business Ethics that govern our decisions and actions in conducting business, it also governs the way PTTEP engage with the associations and delivering values through sustainability initiatives. PTTEP does not have any lobbying activities nor make any contribution, in money or in kind, to political parties or organizations, or to individuals engaged in politics. The Company has disclosed the contribution amount as shown in the Economics Performance Data.
Additionally, PTTEP has been a member of Thailand Responsible Business Network (TRBN) since 2019. TRBN is a non-profit organization and a network of businesses that share the same commitment to drive the country in economic, social and environmental dimensions in compliance with Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). PTTEP also has been a member of Thai Listed Companies Association’s ESG Network.
Leveraging Our Expertise for Public Policy Development
PTTEP acknowledges the significance of driving public policies with government agencies by leveraging its knowledge and initiatives to effectively address national issues such as climate change and biodiversity. PTTEP actively engages with various stakeholder groups through sustainability committees and networks, including:
- CCUS Application Subcommittee under the National Climate Change Policy Committee
- Thailand Carbon Neutral Network (TCNN), led by the Thailand Greenhouse Gas Management Organization (Public Organization), to drive the reduction of Greenhouse Gas (GHG) emissions in collaboration with government sector, private sector, and local communities
- A Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with the Office of Natural Resources and Environmental Policy and Planning and the Department of Climate Change and Environment to launch joint actions on climate change and biodiversity conservation
- An MoU with the Royal Forest Department; the National Park, Wildlife and Plant Conservation Department; Marine and Coastal Resources Department; as well as PTT Group for a two-million-rai reforestation project
- Collaboration agreements with leading university and institutes to foster research and development networks through collectively leveraging their organizational knowledge. Examples include:
- An MoU with Kasetsart University to promote ocean sustainability
- An MoU with the Hydro-Informatics Institute to develop an ocean data platform
- An MoU with Mae Fah Luang Foundation under Royal Patronage to conserve and restore natural resources through community engagement and application of technology for sustainable development
In addition, PTTEP actively engages in relevant Thailand public hearing process such as draft Thailand Climate Change Act, draft Biodiversity Conservation (Areas & Species) Act, and Thailand Taxonomy of the Bank of Thailand (BOT), in which scope and boundary of the current phase does not include oil and gas exploration and production. The progress of the Thailand Taxonomy is being closely monitored to ensure appropriate and timely response of the Company.

